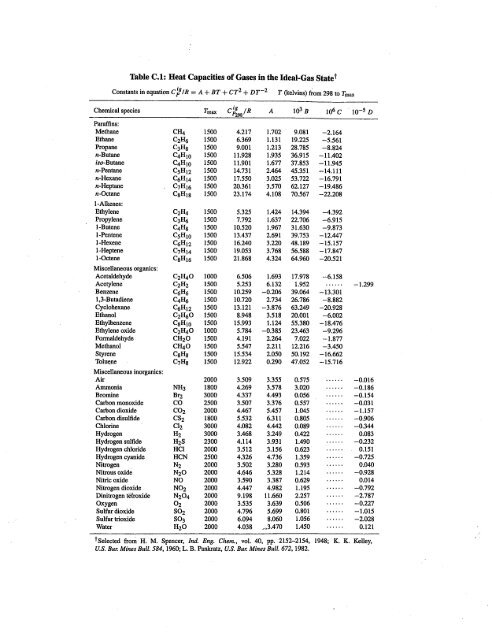
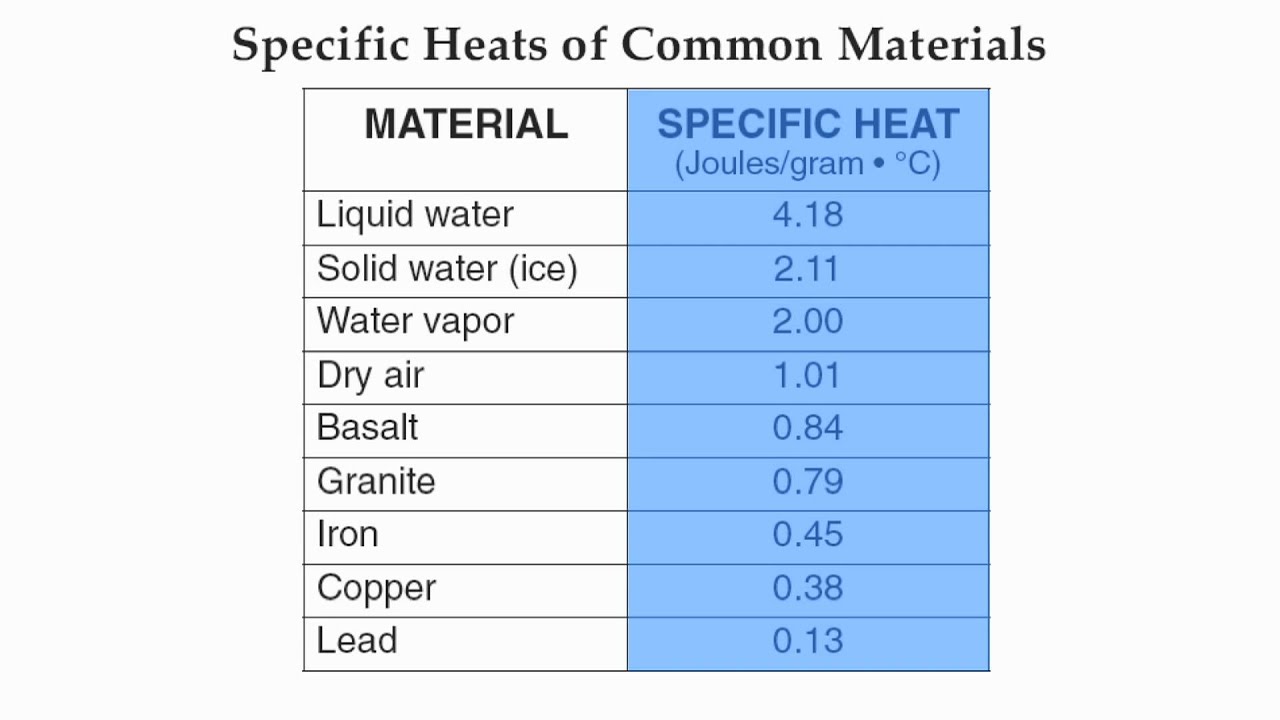
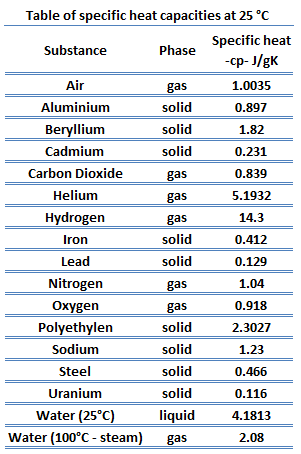
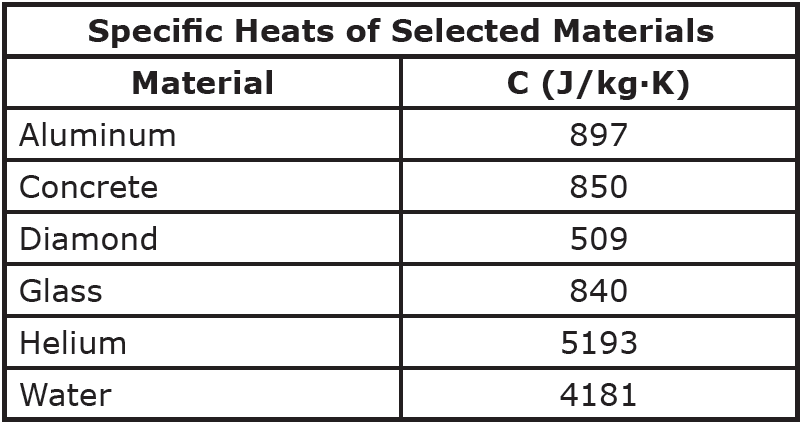
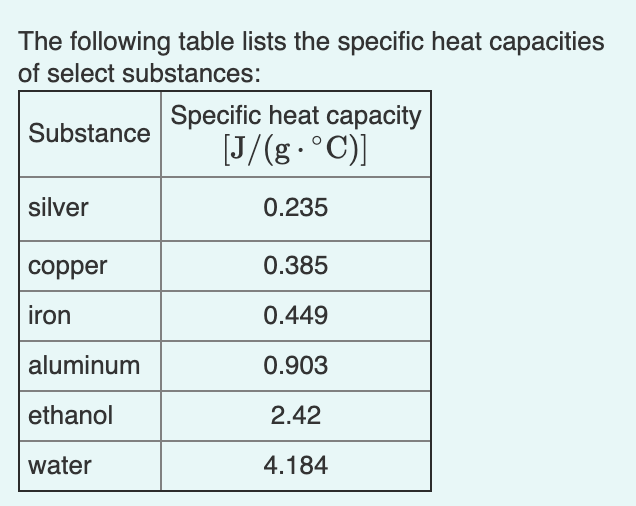
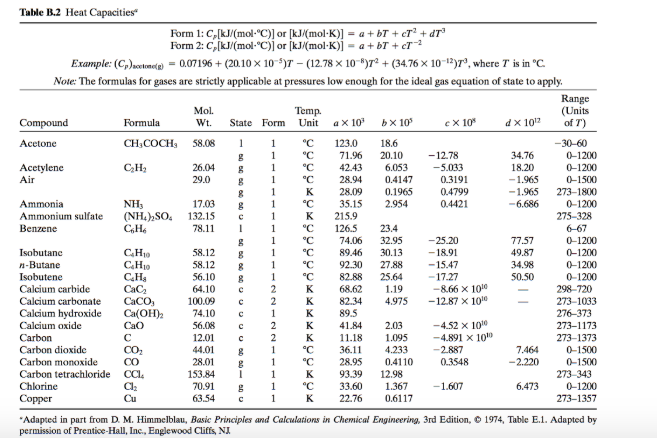
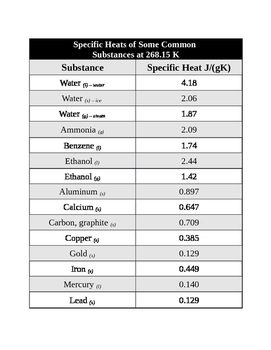
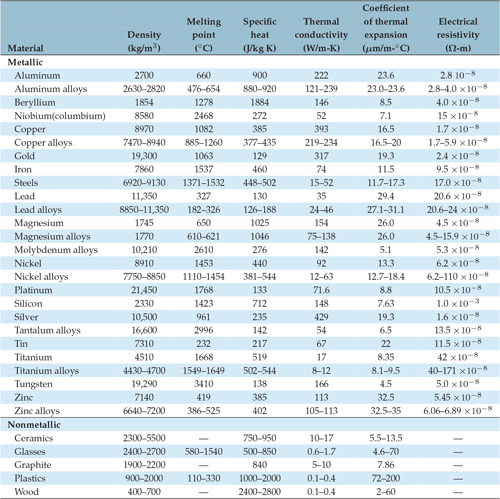
Table of Specific Heat Capacities: List of Thermal Conductivities | PDF | Molar Concentration | Temperature
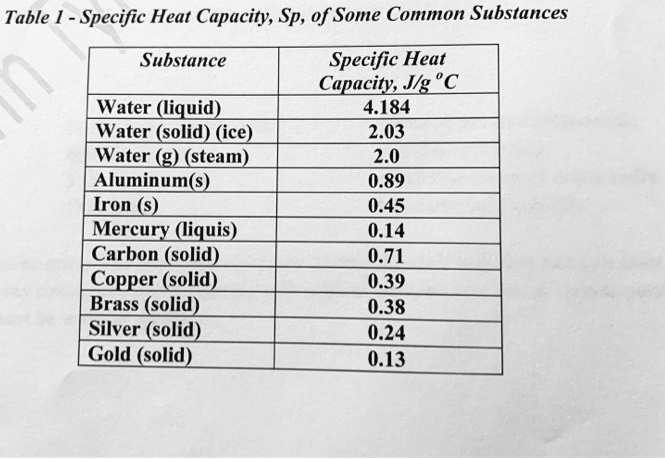
SOLVED: Table 1: Specific Heat Capacity, Sp, of Some Common Substances Substance Specific Heat Capacity, J/g 4.184 2.03 2.0 0.89 0.45 0.14 0.71 0.39 0.38 0.24 0.13 Water (liquid) Water (solid) (ice)
Estimating Heat Capacities for Solutions with Dissolved Solids - Calculations and Tips - Articles - Chemical Engineering - Frontpage - Cheresources.com

Table 1 from Heat capacities and thermodynamic properties of annite ( aluminous iron biotite ) | Semantic Scholar
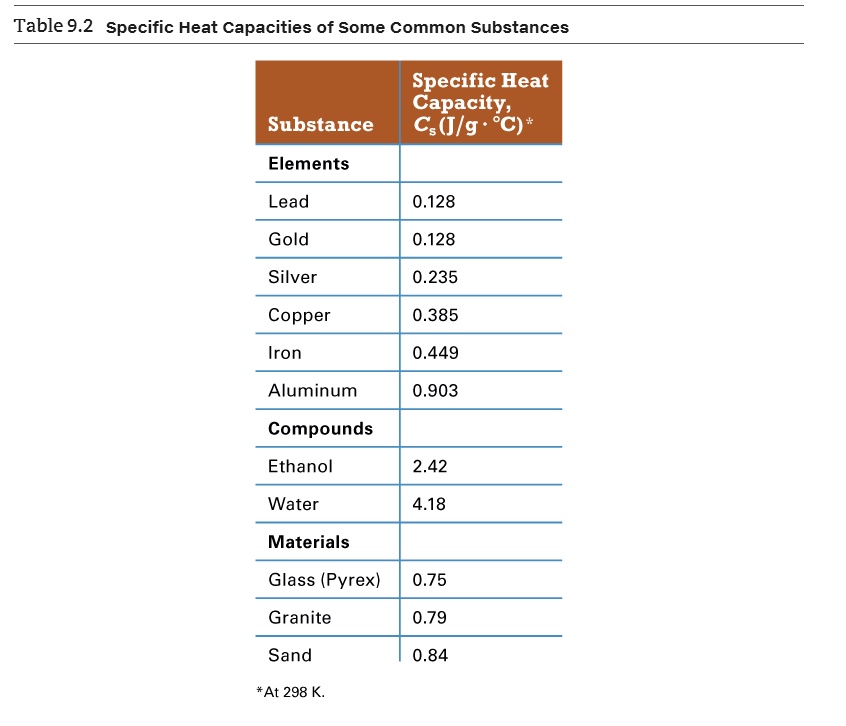
SOLVED: Table 9.2: Specific Heat Capacities of Some Common Substances Specific Heat Capacity; Cs (J/g *°C) Substance Elements Lead 0.128 Gold 0.128 Silver 0.235 Copper 0.385 Iron 0.449 Aluminum 0.903 Compounds Ethanol
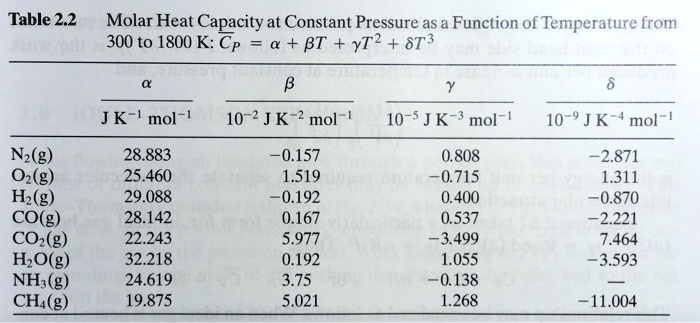
SOLVED: Table 2.2 Molar Heat Capacity at Constant Pressure as a Function of Temperature from 300 to 1800 K: Cp = a + BT + YT^2 + ST^3 JK mol^-1 10^-2 J K^-

![Solved Table B.2 Heat Capacities Form 1: C1kJ (mol·°C)] or | Chegg.com Solved Table B.2 Heat Capacities Form 1: C1kJ (mol·°C)] or | Chegg.com](https://d2vlcm61l7u1fs.cloudfront.net/media%2Fd1e%2Fd1ec8c67-abd1-4bf2-88d0-ce524e9ef2b2%2FphpIIt2ym.png)